
Medication Overview
23 Lessons
Medication Overview
Last activity on February 24, 2026
Cytisine
What it is
- Cytisine is a stop smoking medication. It is in a 1.5mg tablet form, with 1 pack of 100 tablets being taken over a course of 25 days.
How it works
- It acts as a partial agonist, blocking receptors in the brain involved in nicotine dependency, reducing urges to smoke, working in a similar way to Champix.
When do you quit smoking
- Quit date should be set no later then day 5 of starting the treatment
How to take it
- Swallow whole with water. Follow the schedule below:
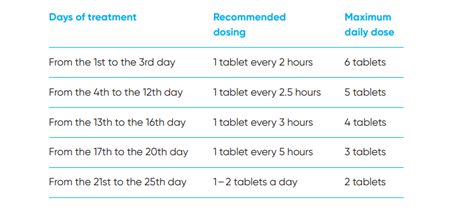
- NCSCT guidance for Cytisine
Cytisine Contraindications:
- renal (kidney) impairment
- hepatic (liver) impairment
- over 65 years of age
- under 18 years of age
- hypersensitivity to Cytisine or any of the excipients (non-active ingredients)
- unstable angina (chest pain caused by reduced blood supply to the heart)
- a history of recent myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- clinically significant arrhythmias (irregular or abnormal heart rhythm)
- had a recent stroke
- pregnant or breastfeeding
Please note:
Cytisine should not be used with anti-tuberculosis drugs.
Women of childbearing age using hormonal contraception should add a secondary barrier method whilst taking Cytisine as it is unknown whether Cytisine may reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives.
Cytisine Cautions:
- ischemic heart disease
- heart failure
- hypertension (high blood pressure)
- pheochromocytoma (tumor in the adrenal glands)
- atherosclerosis (thickening or hardening of the arteries) and other peripheral vascular diseases.
- gastric and duodenal ulcer
- gastroesophageal reflux disease
- hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
- diabetes
- schizophrenia
Side effects
Very common (may affect more than 1 user in 10)
change in appetite (mainly increase), weight gain, dizziness, irritability, mood changes, anxiety, hypertension, dry mouth, diarrhoea, rash, fatigue, sleep disorders (insomnia, drowsiness, lethargy, abnormal dreams, nightmares), headaches, tachycardia, nausea, alters some flavours, heartburn, constipation, vomiting, abdominal pain (especially in the upper abdomen), muscle pain.
Common (may affect 1 to 10 users in 100):
difficulty in concentration, slow heart rate, abdominal distension, burning tongue, malaise.
Uncommon (affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000): feeling of heaviness in the head, decreased libido, lacrimation (abnormal or excessive secretion of tears), dyspnoea (shortness of breath), increased sputum (phlegm), excessive salivation, sweating, decreased elasticity of the skin, tiredness, increase in serum transaminase levels
Using Cytisine and smoking or using nicotine containing products (nicotine replacement therapy (NRT), nicotine vapes, nicotine pouches etc) could lead to aggravated side effects.